What is Ozone Therapy?
 Ozone is an unstable gas molecule made up of three oxygen atoms. Ozone is in the outer layer of the atmosphere and protects living organisms by absorbing harmful rays from the Sun. It has been discovered in the 18th century. Scientists has unveiled the importance of ozone over the years and it has gained ground in industrial and medical practices. It is a strong oxidative molecule with a lethal effect on bacteria. This paved the way for the use in many fields.
Ozone is an unstable gas molecule made up of three oxygen atoms. Ozone is in the outer layer of the atmosphere and protects living organisms by absorbing harmful rays from the Sun. It has been discovered in the 18th century. Scientists has unveiled the importance of ozone over the years and it has gained ground in industrial and medical practices. It is a strong oxidative molecule with a lethal effect on bacteria. This paved the way for the use in many fields.
Medical ozone therapy is defined as the administration of ozone gas for the treatment of the disorders and in some cases, for supporting the treatment of the disorders. This method is mainly developed in Italy. Ozone is a highly toxic gas. Thus, it is not administered as a single agent but it is combined with oxygen. The mixture is composed of mainly oxygen and a small portion of ozone (approximately 20 mcg/ml). This ratio depends on the disorder and administration method (1 – 60 µg/ml).

The Effects of Ozone Therapy on Human Body
 Ozone may effect locally or generally, depending on the route of administration. In the most preferred therapy method, called major autohemotherapy, patient’s blood is withdrawn, ozone gas is infused into the blood and the blood is then given back to the patient. In this procedure, when the ozone-oxygen mixture is infused into the blood, the majority of the oxygen binds to hemoglobin and some portion dissolves in plasma. Ozone turns into oxygen and oxygen radicals in only a couple of seconds and the blood no longer includes free ozone molecules. This way, the venous blood includes high level of oxygen and peroxides. The blood can be given back to the patient now. After that, the oxygen radicals react with blood plasma resulting in peroxide formation. Hydrogen peroxide in the blood acts as a metabolism stimulant and rapidly diffuses into cells. It is the most significant agent for the therapeutic effects of major autohemotherapy. The generated oxygen radicals lead to the oxidization of molecules with antioxidant features in blood plasma such as urea, uric acid and albumin. This process temporarily changes the redox equation of the plasma. This is called as therapeutic shock. This process triggers the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the body and represents the majority of the therapeutic effects of the ozone therapy. This process also includes oxidization of unsaturated fatty acids which then diffuses into various tissues and activates immune system and bone marrow.
Ozone may effect locally or generally, depending on the route of administration. In the most preferred therapy method, called major autohemotherapy, patient’s blood is withdrawn, ozone gas is infused into the blood and the blood is then given back to the patient. In this procedure, when the ozone-oxygen mixture is infused into the blood, the majority of the oxygen binds to hemoglobin and some portion dissolves in plasma. Ozone turns into oxygen and oxygen radicals in only a couple of seconds and the blood no longer includes free ozone molecules. This way, the venous blood includes high level of oxygen and peroxides. The blood can be given back to the patient now. After that, the oxygen radicals react with blood plasma resulting in peroxide formation. Hydrogen peroxide in the blood acts as a metabolism stimulant and rapidly diffuses into cells. It is the most significant agent for the therapeutic effects of major autohemotherapy. The generated oxygen radicals lead to the oxidization of molecules with antioxidant features in blood plasma such as urea, uric acid and albumin. This process temporarily changes the redox equation of the plasma. This is called as therapeutic shock. This process triggers the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the body and represents the majority of the therapeutic effects of the ozone therapy. This process also includes oxidization of unsaturated fatty acids which then diffuses into various tissues and activates immune system and bone marrow.
Contraindications of Ozone Therapy
Contraindicated in following conditions: Massive bleeding, coagulopathies, frequently recurrent acute pancreatitis, allergy, glucose 6P dehydrogenase enzyme deficiency (broad beans).
Direct inhalation of ozone gas is prohibited.
What Are The Methods of Administration?
Paravertebral ozone injection:
It is the most preferred method of administration for ozone therapy in our clinic but in medical environments, major autohemotherapy is more preferred over this method. Paravertebral ozone therapy is administered by injecting the ozone-oxygen mixture into the muscles around the spine for the treatment of spinal and cervical disc herniation. This procedure takes approximately 30 seconds and it may be performed 1 to 3 times in a week depending on the severity of the disorder. Most of the patients recover upon 10 sessions. The number of the administrations may vary from 5 sessions, for mild cases, to 20 sessions, for very severe cases. The patient may feel pain during the injection but it stops in a couple of minutes. Paravertebral ozone injection can provide very good results and a rapid recovery period for the treatment of spinal and cervical disc herniations.
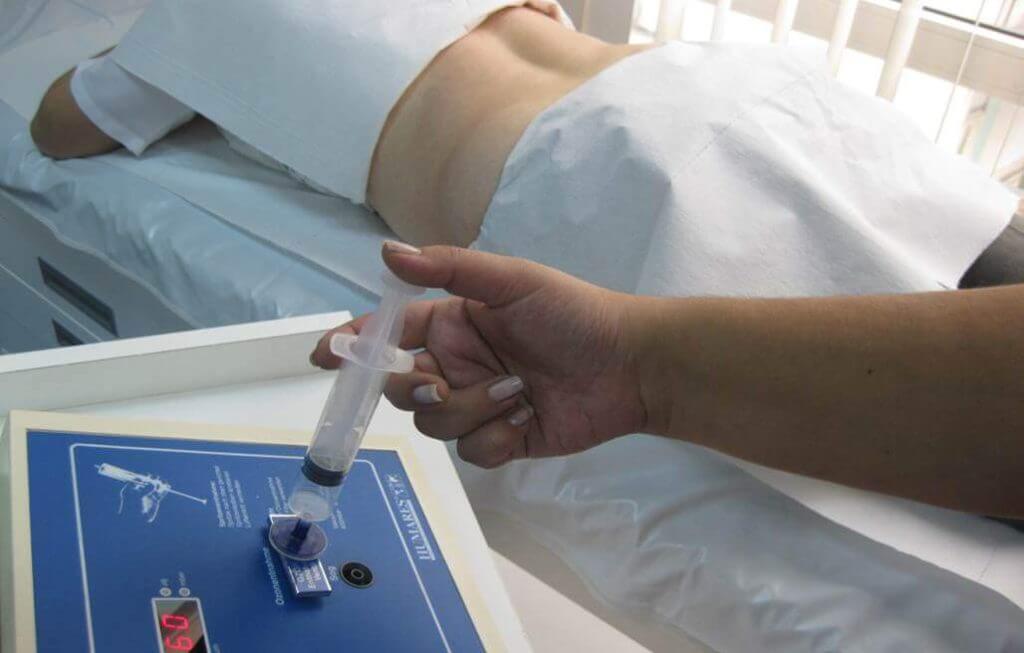
Major Autohemotherapy
This is the most preferred method of administration. The patient’s blood (about 50-120 ml) is withdrawn into a sterile tube that is resistant to ozone. An appropriate amount of ozone-oxygen mixture is infused into the blood and then this blood is given back to the patient. Major autohemotherapy is the primary method of administration and takes approximately 20 minutes.
Watch Major Autohemotherapy Video
Minor Autohemotherapy
It includes the intramuscular administration of ozone and a small portion of blood mixture. It is not a highly preferred method.

Intra-articular Injection
Generally, 3-5 intra-articular gaseous injections (ozone-oxygen mixture) are administered into the joints with osreoarthritis. This method is especially preferred for the treatment of knee arthrosis.
Watch Paravertebral Injection Video
Local Injection
Ozone-oxygen injection is administered into myofascial trigger points and painful intramuscular trigger points. Generally 1-3 injections provide benefit. A similar administration can be preferred for tendon rheumatism. It is an unfavorable procedure due to the pain.
Intradiscal Injection
It is a special form of ozone-oxygen injection with long needles into the disc under fluoroscope or tomography in an operating room environment for patients with spinal disc herniation. This operates by minimizing the herniation. It is performed by pain specialists. Successful results can be achieved with minor complications. Other disadvantages of the procedure can be listed as exposure to radiation and the high cost.
Bagging
This method is mainly preferred for the treatment of non-healing bedsores and diabetic foot ulcers, and gangrene. The body part is isolated by surrounding with a bag and introducing ozone-oxygen mixture. This way, the gaseous mixture contacts with the wound and provides a therapeutic effect.
Rectal Insufflation
Rectal administration of ozone in patients ineligible for intravenous administration.
Ozonated Water
Administered with ozonated physiological saline solution. This method is especially used for washing infected wounds.
Ozonated Olive Oil
Ozonated Olive Oil is used for skin lesions.
Ozone Sauna
Mostly preferred for cosmetic purposes.
Ozone Therapy Indications
Musculoskeletal System
Spinal and cervical disc herniations, myofascial pains, knee arthrosis (injection). It’s effect has been proven with many scientific researches, especially for the treatment of spinal disc herniations.
Circulatory System
Arterial occlusion and stenosis on the lower extremities, other circulatory disorders, wounds secondary to circulatory disorders (major autohemotherapy), diabetic foot ulcer, infected wounds, bedsores, burns, non-healing wounds, osteomyelitis.
Eye Diseases
Macular degeneration
Cosmetic Applications
Anti-aging, skin resurfacing
Weight Loss
Streamlines weight loss by boosting metabolism, supporting regimen and exercises. It is also used for overcoming stress, mental and physical chronic fatigue syndrome and high consumption of cigarette in healthy individuals.

