Neurological Rehabilitation
 Neurological disorders represent the widest area in rehabilitation medicine. Due to the lack of an effective medicinal treatment for the majority of the neurological disorders,
Neurological disorders represent the widest area in rehabilitation medicine. Due to the lack of an effective medicinal treatment for the majority of the neurological disorders,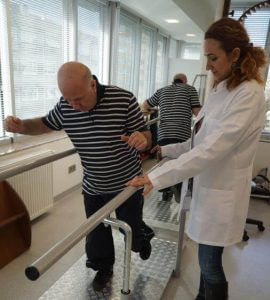 it is only possible through rehabilitation to maximize the patient’s functional capacity and to teach the patient how to leverage that capacity.
it is only possible through rehabilitation to maximize the patient’s functional capacity and to teach the patient how to leverage that capacity.
Neurological rehabilitation can be utilized in a number of primary disorders. Neurological rehabilitation is effective in patients suffering from stroke due to occlusion of an artery or bleeding into brain tissue (hemiplegia, stroke); traumatic brain injury; cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis; parkinson’s disease; spinal injuries (paraplegia; paraparesis); hereditary neurological disorders (polyneuropathy; degenerative brain disorders, ataxia); genetic or inherited muscle disorders (myopathies, muscular dystrophy); paralysis secondary to brain tumors and surgeries; Guillian-Barre syndrome; motor neuron disorders; patients who have fallen due to muscle weakness, imbalance and dizziness in old age.
Especially the conditions developed upon occlusion of an artery in brain, bleeding into brain or direct brain damage usually lead to paralysis on one side of the body. In these cases, the size of the area affected is the main factor for the recovery potential but rehabilitation also has a significant effect on the level of function for the future. Although medicinal therapy is essential for multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s diseases, which also have a high prevelance rate, there is a limit on the benefits of medicinal therapy. Medicinal therapy is not effective on spinal cord disorders, injuries and myopathies.
Patients are treated with neurological rehabilitation for falling due to muscle weakness, imbalance and dizziness in old age and exercise provides significant benefits for these types of patients. Essentially patients experience various changes due to low or no mobility in all neurological disorders that affect brain, spinal cord, nerves and muscles. Muscle weakness stands out among these disorders. Patient may also experience additional manifestations such as severe muscle spasticity, sensory loss, imbalance, involuntary movements. Medicinal therapies show little or no efficacy in such conditions. Medicines cannot strengthen the muscles for these patients. The patients mainly benefit from rehabilitation programs. These include various methods of therapy. Some of the methods used commonly for these patients can be listed as standard exercise methods (stretching, strengthening and balance exercises), special neurophysiological exercises, computer assisted rehabilitation therapies, and robotic rehabilitation. For patients with severe muscle spasticity, muscle relaxant botox injections are administered when necessary. Adjuvant equipments (orthesis) that streamlines walking may also be prescribed for eligible patients. These methods among many of the therapy options can maximize the patient’s level of function.
 The rehabilitation process should be initiated from day one. The important thing is to initiate the treatment process as soon as possible. After discharging from the hospital, the patient should continue treatment at home and start visits to physiotherapy centers when he/she is able to do so. If the patient is not able to visit the physiotherapy center, the physiotherapists should maintain the therapy process by visiting the patient at home and training the relatives about the process. It is extremely important for the family to involve in the treatment process in the cases of patients with cerebral palsy and patients that are not able to visit the physiotherapy center. It is really sad to encounter many patients who are confined to bed and their relatives simply because they are not provided with rehabilitation therapies in our country. The patients with neurological disorders, even when they are really old, should not be left to their fate. This would cause significant consequences for the patients and also their relatives.
The rehabilitation process should be initiated from day one. The important thing is to initiate the treatment process as soon as possible. After discharging from the hospital, the patient should continue treatment at home and start visits to physiotherapy centers when he/she is able to do so. If the patient is not able to visit the physiotherapy center, the physiotherapists should maintain the therapy process by visiting the patient at home and training the relatives about the process. It is extremely important for the family to involve in the treatment process in the cases of patients with cerebral palsy and patients that are not able to visit the physiotherapy center. It is really sad to encounter many patients who are confined to bed and their relatives simply because they are not provided with rehabilitation therapies in our country. The patients with neurological disorders, even when they are really old, should not be left to their fate. This would cause significant consequences for the patients and also their relatives.
Orthopedic rehabilitation
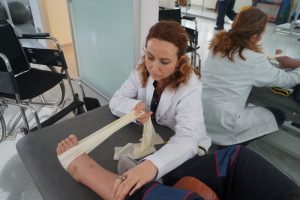 Orthopedic rehabilitation covers all rehabilitation efforts performed following any type of orthopedic intervention (cast, surgical operation etc.) for the treatment of medical conditions due to a musculoskeletal disorder or trauma.
Orthopedic rehabilitation covers all rehabilitation efforts performed following any type of orthopedic intervention (cast, surgical operation etc.) for the treatment of medical conditions due to a musculoskeletal disorder or trauma.
Thus, orthopedic rehabilitation includes a wide scope. All cases of fracture; dislocation; joint stiffness and deformities due to cast and immobility; anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction; knee, hip and knee replacement; knee and hip arthroscopy; sports injuries; amputations (upper or lower extremity); Achilles tendon repair surgery; tendon and nerve repair surgeries in hands and feet; deformity correction surgery (hip dislocation, toe deformities etc) are among the common conditions that require orthopedic rehabilitation. Orthopedic rehabilitation is as important as the orthopedic surgery itself and has a direct impact on the success of the surgery. The common thread to all orthopedic interventions (cast, surgery, slings etc.) is the limitation on the mobility of the operation site. Human body is designed for continues mobility and severely harmed in cases of immobility. Soft tissue shortening and stiffness occurs on the restricted body parts. The level of the stiffness is directly proportional to the duration of immobility. Shortening and stiffness of the soft tissues result in joint stiffness and joint contractures.

This condition, “contracture”, is one of the main factors to define the success of the orthopedic intervention. Another significant issue we encounter upon orthopedic surgeries and the subsequent immobility is muscle weakness (atrophy). When muscles are not used for a month, approximately 30% is wasted on the muscular volume and strength. Thus, orthopedic rehabilitation targets these two main conditions, joint stiffness and atrophy, occurring on the joints and peripheral body parts due to long term inactivity. Currently, the subsequent inactivity period is one of the main elements for the choice of bone & joint surgeries and also tendon surgeries. For example, in the case of a femoral fractures, intraosseous nailing is preferred over plaster casts. For plaster cast, the treatment period (bone union) extends to 2-3 months and upon the removal of the cast, the patient may be left with incurable joint stiffness, especially on the knees. Fır intraosseous nailing, the patient can resume their daily activities after a short period of time and bone union is achieved much faster. Since this method allows a limited level of activity, the patient does not suffer from joint stiffness.

Unfortunately, there are quite many orthopedists in our country who still has not fully comprehended the significance of orthopedic rehabilitation. They do not recommend rehabilitation after the removal of plaster casts and surgeries to the patients and in some cases they just suggest home exercises. Nevertheless, it is not possible for the patients to recover the damage with just home exercises. In the cases of some special surgeries, such as tendon surgeries, physical therapy is indispensable. The longer it takes to initiate the rehabilitation program after any orthopedic intervention, the harder it gets to recover from the joint stiffness occurred due to inactivity. Please note that all orthopedic interventions require rehabilitation and rehabilitation is a significant factor for the outcome of the therapy.

