admin
Special Injections
Special injections are among the most significant therapies. The medications administered into the injection site speeds up the process. It is a highly preferred treatment choice with reduced labor and costs. Under the scope of physical therapy, local injections can be administered for joint diseases (intraarticular, periarticular), trigger points in the muscles, spinal painful diseases and soft tissue disorders (tendons, ligaments, nerves). Mostly cortisone, local anesthetics, Na hyaluronate, special medication mixtures (prolotherapy), botulinum toxin (botox, dysport), PRP (platelet rich plasma), ozone are preferred for these injections. In some cases needling without medication or injection may provide relief (dry needling).
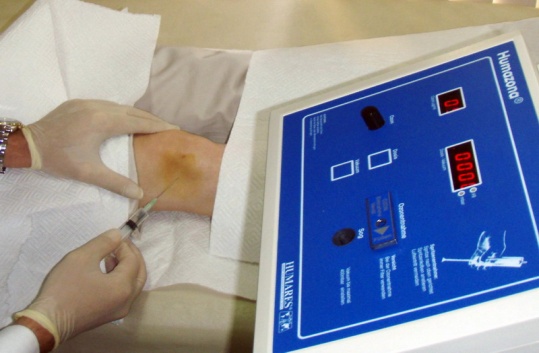
Cortisone Injections
Administered into soft tissues and intra-articularly. Usually given with local anesthetics for pain relief and a good level of distribution. This is by far the most preferred injection method and provides a high level of efficacy. Patients do not experience the majority of the side effects of cortisone as it is only administered single dose. In some cases, high blood pressure may cause temporary increases in blood glucose and flushes for patients with diabetes. These side effects can be controlled and thus, cortisone injections are highly safe. Arthritis, special joint diseases (shoulder, knee), tendon and ligament disorders (tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, tendinitis), special spinal disorders, spinal and cervical disc herniations are among the common disorders for which local cortisone injections are administered. It can be administered up to 4 times for a particular joint but usually, 1 injection provides efficacy for about 6 months to 1 year. It provides a high level of efficacy in tendon injections and a single dose can provide a permanent relief. In some disorders such as tennis elbow about 30-40% of the patients may experience relapse.
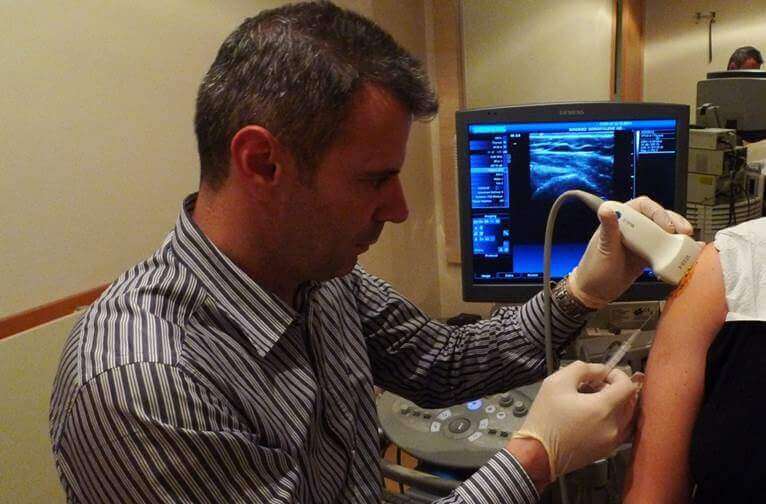
Na Hyaluronate (Cartilage Injection)
 A special injection administered intra-articularly. A lubricant fluid with high molecular weight, including Na Hyaluronate which is one of the primary materials of joint cartilage. This fluid covers the cartilage surfaces decreasing the friction coefficient of cartilage damaged due to arthrosis. Single dose and triple-dose injections (with one-week intervals) are commercially available. It should be repeated with 6 months-1 year intervals since it only provides temporary relief. It is most commonly administered into the knee while it is also injected into hip, shoulder, mandibular joint, wrist-thumb joint. Except from local allergy reactions for a couple of days with a low incidence rate, there are no side effects.
A special injection administered intra-articularly. A lubricant fluid with high molecular weight, including Na Hyaluronate which is one of the primary materials of joint cartilage. This fluid covers the cartilage surfaces decreasing the friction coefficient of cartilage damaged due to arthrosis. Single dose and triple-dose injections (with one-week intervals) are commercially available. It should be repeated with 6 months-1 year intervals since it only provides temporary relief. It is most commonly administered into the knee while it is also injected into hip, shoulder, mandibular joint, wrist-thumb joint. Except from local allergy reactions for a couple of days with a low incidence rate, there are no side effects.
Ozone Injection
 Ozone injection is the direct injection of low level of ozone and oxygen mixture into the relevant site. Ozone injection causes various physiological impacts on the injection site. It inactivates chemicals that cause pain, provides anti-rheumatic effects and relief. Ozone injection is preferred in the treatment of spinal and cervical disc herniation, myofascial pain (muscle cramps) and arthrosis. It is especially used in the cases of knee arthrosis. Usually administered 3-5 doses with a couple of days intervals. It can provide efficacy of several months to a year. Ozone injection is most commonly used in the cases of spinal and cervical disc herniation. Especially for the cases of spinal disc herniation, ozone injection into the paraspinal muscles is highly effective and provide pain relief even with just one dose. This method provides efficacy for patients with acute sciatica pain in the legs. It is administered at least 6 doses with several days of intervals for mild cases and 10 doses -and rarely more- for severe cases. There is almost no side effect of ozone injection. Intra-articular injections are relatively pain-free while muscular injections may cause temporary pain for some cases.
Ozone injection is the direct injection of low level of ozone and oxygen mixture into the relevant site. Ozone injection causes various physiological impacts on the injection site. It inactivates chemicals that cause pain, provides anti-rheumatic effects and relief. Ozone injection is preferred in the treatment of spinal and cervical disc herniation, myofascial pain (muscle cramps) and arthrosis. It is especially used in the cases of knee arthrosis. Usually administered 3-5 doses with a couple of days intervals. It can provide efficacy of several months to a year. Ozone injection is most commonly used in the cases of spinal and cervical disc herniation. Especially for the cases of spinal disc herniation, ozone injection into the paraspinal muscles is highly effective and provide pain relief even with just one dose. This method provides efficacy for patients with acute sciatica pain in the legs. It is administered at least 6 doses with several days of intervals for mild cases and 10 doses -and rarely more- for severe cases. There is almost no side effect of ozone injection. Intra-articular injections are relatively pain-free while muscular injections may cause temporary pain for some cases.
Watch Ozone Injection Video
Injections of Local Anesthetics
It is usually administered with a mixture of cortisone,. This is one of the most preferred methods for the treatment of myofascial pain trigger points (shoulder pain – muscle cramp). For the treatment of such muscle pain, it is usually given in several doses of 1-2 cc and provides a high level of efficacy in combination with stretching exercises. There are rare side effects due to the low amount of medication it includes. In some cases, it may be given to reveal the source of pain while it may be used to relieve pain prior to some treatments.
Watch Injections of Local Anesthetics Video
Btulinum Toxin (Botox Injections)
Botulinum toxin is a very poisonous toxin of some kind of a bacteria. It causes a certain level of paralysis on the muscle, impacting on the neuromuscular transmission. Paralysis lasts 3-4 months. Thus, this method is preferred for the treatment of severe muscle spasticity developed in the cases of palsies (stroke, hemiplegia, paraplegia, spastic paraplegia), involuntary movements, muscle spasticity in children with cerebral palsy, distonia (writer’s cramp, musician’s cramp), tension-type headache, heavy sweating in hands. It is also used very commonly for eliminating wrinkles in cosmetics sector. In rehabilitation medicine, it is most commonly used for the treatment of muscle spasticity developed in cases of strokes. The relevant muscle is numbed for 3-4 months to improve the efficacy of rehabilitation in the meantime. The physician may decide repeating the injections based on the condition and response to the treatment. For young children, it is usually administered under anesthesia. There are no side effects unless administered with a high dose. The antibodies produced upon repetitive injections may decrease the efficacy of the injection. The most outstanding disadvantage of the method is its high cost.
Watch Btulinum Toxin (Botox Injections) Video
ESWT (Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy) is a relatively new treatment method aiming to accelerate recovery and minimize pain by submitting shock waves to damaged tissues for painful musculoskeletal conditions.
Shock waves are submitted via a metal applicator with pressurized air. A special attachment that moves fast within the metal head produces shock wave at the end of the probe. The size and shape of the end of the probe vary on the application site. The energy level and frequency can be adjusted. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy used in the musculoskeletal conditions utilizes the same mechanism with 10-fold lower energy.
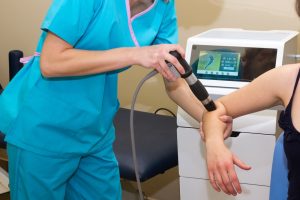
The effect of ESWT on the tissues
The mechanism action of ESWT that reduces pain is not known. Theoretically, it is assumed that ESWT disrupts fibrous tissue generation on the relevant site and improves blood circulation, promoting recovery. It is also another theory that shock waves block neural transmission of pain to the brain.
The disorders treated with ESWT
Achilles tendinitis, enthesitis
Plantar fasciitis (calcaneal spur)
Calcific tendinitis of the shoulder
Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)
Medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow)
Tendonitis of the foot Chronic plantar fasciitis (plantar fibromatosis)Nonunion of fracture Myofascial muscle pain Unhealed ulcerous skin scars
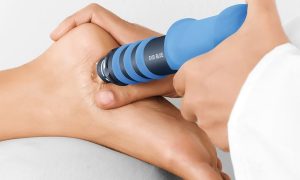
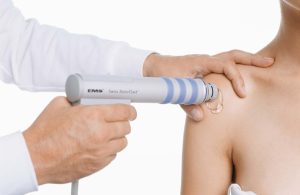
How Administered
ESWT is usually administered for 3-5 times at intervals of 5-7 days. The physician determines the duration and parameters (duration, frequency and pressure) of the therapy based on the patient’s condition. Some patients may benefit from the treatment at the first session while chronic patients benefit after a couple of sessions. It is possible to achieve a higher level of success when combined with other physical therapy methods and exercise.
Are there any side effects of ESWT?
ESWT does not cause any harm to the body. It does not require application of anesthesia for the treatment site. In some cases, the patient may feel some pain but this will go away after a couple of sessions. There may be mild rash and swelling at the treatment site. Except for the limited daily activities, the patient does not need to enter a special recreation period.
Definition of Pain
Pain is defined as “an unpleasant sense that covers all prior experiences of an individual with or without any organic reason that originates from any part of the body”. Pain is essentially a sensation which enables the individual to be aware of the processes in their body. For example, a patient with appendicitis is alerted with abdominal pain. Without the pain, the patient would only become aware after the fever due to the infection of periton that is caused by the perforation of appendicitis.

Does Everyone Feel the Same Pain?
As stated in the definition, pain is a very complex sensation. It may result from an organic reason, which is any condition that harms the body (illness, trauma etc.). However, an organic reason is not the prerequisite for pain. There are also patients suffering with no possible medical explanation. Thus, pain may also result from psychological reasons. It is essentially a sensation. Each brain comprehends pain differently. For example, a patient feels no pain upon an injection while others suffer badly. It is explained with the concept of “pain threshold” in modern medicine. Meaning, there is a threshold for each person to comprehend a stimulus as “pain” and this threshold is different for everyone. It has been determined by applying a gradual pressure to the same sites in the body with a special pressure gauge (illustration) that the threshold for comprehending a sense of pressure as pain is different for each person. And this shows that pain is a personal sensation.
The History of Pain Management
It is quite understandable that pain management may be very challenging in some cases due to the complexity of pain. The history of pain management dates back to centuries ago. Herbal medicines and heat & cold applications are among the very first methods for pain management. Alpha salicylic acid (aspirin) extracted from willow bark underlies modern painkillers. The introduction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with remarkable studies in pharmacology is the groundbreaking advancement in pain management. This has been followed with the exploration of opioids and strong analgesics that are categorized as narcotics and sold with green/red prescription. Local anesthetics are medicines that block the sense of pain on the administration site for a certain time. Local anesthetics enable us to perform small surgical interventions, dental interventions without any pain to the patient. General anesthetics on the other hand enable us to perform surgeries without any pain by completely controlling the pain. For the last century of the history of pain management, many physical therapy methods have been developed and conventional methods are employed within the framework of modern medicine (illustrations; conventional and modern vacuum therapy). Physical therapy methods are highly utilized for pain management for the last thirty years.

Which Groups of Specialists Provide Pain Management?
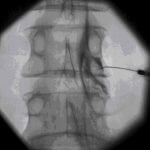
Pain is classified to determine the treatment protocols. Pain can be classified as acute pain and chronic pain based on the occurrence rate and somatic pain, psychosomatic pain and neuropathic pain based on the origin. It may be required for the patient to be treated by multiple physicians based on the origin of the pain (multi-discipline approach). A stomach ache might be relevant for an internal specialist, a general surgeon an a rheumatologist from time to time. However, the most common origin of the pain is musculoskeletal system and thus, the major group of specialists dealing with pain management is physical therapy specialists in our country. Recently, physical therapy, anesthesiologist and neurology specialists are provided with the opportunity to become a specialist in pain management by taking an additional 2 years-of training. Pain management specialists provide some special interventions in addition to the therapies presented by physical therapy specialists. These interventions are mainly spine-cervical vertebra injections in combination with fluoroscopy or CT.
Which Methods are Utilized in Pain Management?
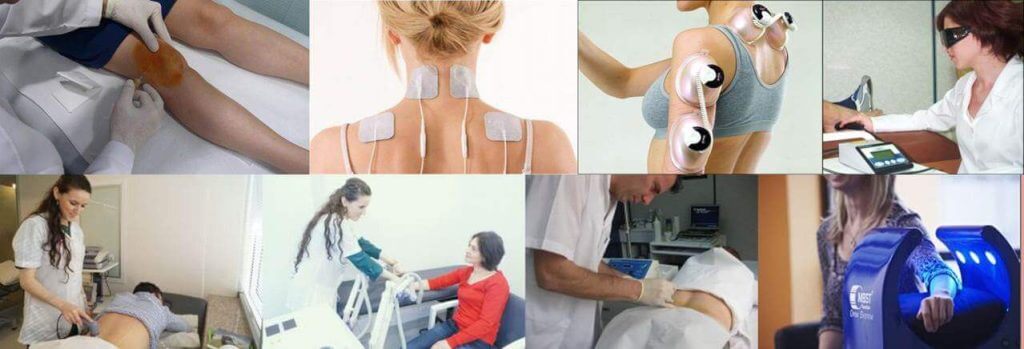
Simple analgesics, anti-rheumatoid medications, opioid and narcotic analgesics (addictive drugs), antidepressants, neuropathic medications, cortisone, ozone injection, physical therapy methods (TENS, low frequency current, ultrasound etc.), special injections (spine, soft tissue, intraarticular injections, botox injections) are among the most commonly used methods in pain management.
Pain is a complex sensation and determining the source of the pain is the most important step of the treatment. Only after that, one or several of the methods above can be utilized for pain management.
What is the explanation of rheumatic disease ?
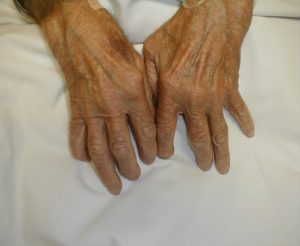
Rheumatic diseases are generally described as disorders caused by an inexplicable disorder of the immune system (autoimmune) that generally affect the joints and sometimes internal organs. Numerically, there are actually only a limited number of diseases. However, same rheumatic disease can have various differenet manifestations in individuals. Cases of osteoarthritis are included in this category while its action mechanism is highly different from the autoimmune system triggered rheumatism diseases.
What Are The Causes of Rheumatic Diseases?
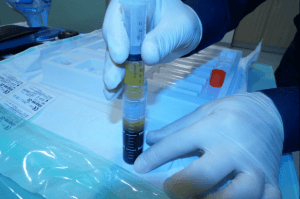 The causes of the diseases in this group has not been fully discovered yet. It is believed that these diseases are triggered by environmental factors in patients with genetic predisposition. For example, for some rheumatic diseases, the members of the same family are at higher risk of developing these diseases. However, it is also possible that one of the twins develop rheumatic diseases while the other does not. This suggests that the causes cannot be explained by genetics. An agent (usually viruses) causes the body to somehow produce substances that harm the joints and tissues. Indeed, immune suppressive drugs provide recovery from the symptoms of inflammatory rheumatism diseases.
The causes of the diseases in this group has not been fully discovered yet. It is believed that these diseases are triggered by environmental factors in patients with genetic predisposition. For example, for some rheumatic diseases, the members of the same family are at higher risk of developing these diseases. However, it is also possible that one of the twins develop rheumatic diseases while the other does not. This suggests that the causes cannot be explained by genetics. An agent (usually viruses) causes the body to somehow produce substances that harm the joints and tissues. Indeed, immune suppressive drugs provide recovery from the symptoms of inflammatory rheumatism diseases.
What Are The Most Common Rheumatic Diseases?
Two primary diseases stand out in this group: rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. These two diseases represent almost over 80% of the rheumatology practice. Psoriatic arthritis, sjogren’s syndrome and gut are among the other common inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Other spondylopathies (inflammatory spinal rheumatisms); spondylopathies secondary to inflammatory bowel disease; and psoriatic spondylopathies are relatively rare. Cases of juvenile arthritis developed in childhood period are also not common. Systemic lupus eritomatozus in accompany with internal organ involvement, systemic sclerosis, vasculites (Behçet’s disease) are relatively rarely encountered types of inflammatory rheumatism.
Who Can Provide Treatment for Inflammatory Rheumatism Patients?
Rheumatology and physical therapy doctors (physiatrists)vcan provide treatment for the patients in this group. A rheumatology doctor is a physical therapy or internal diseases specialist with an addition of 2 years master degree in rheumatology. Hence, some of the rheumatologists are doctors specialized in physical therapy while some are doctors specialized in internal diseases. Up until the last 15-20 years in our country, physical therapy specialists would provide treatment for rheumatic diseases. The reason is that residency training for this branch included the treatment of rheumatic diseases. With the increase in the number of rheumatology specialists, some of the physical therapy specialists providing treatment in this patient group have started to decrease. While the others kept on this practice. In the light of this fact, the Ministry of Health granted physical therapy specialists without a masters degree the authority to prescribe almost all medicines used in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. And this enabled physical therapy specialists familiar with the current advancements in rheumatic diseases who practice both in private and public and university hospitals to achieve treatments for patients in this group.
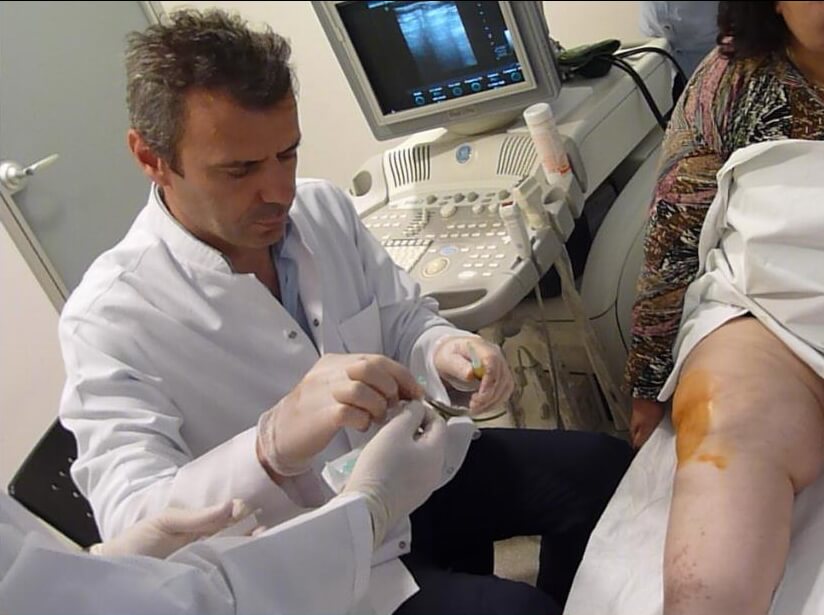
Are Drugs The Only Treatment Option For Rheumatic Diseases?
Drugs are of importance for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, for sure. Especially for the last decade, we have more treatment alternatives in alignment with the advancements in treatment with biological agents. Nonetheless, exercise is actually a crucial treatment option for the patients in this group but it is usually underrated by the doctors. Drugs may provide regression for the joint inflammation but they also have limited effect on correcting joint deformities and regaining joint functions. Thus, these patients must be prescribed with a preventive exercise program. Rheumatic diseases are chronic and disabling disorders. Thus, it is of crucial importance that these patients are early diagnosed, prescribed with an appropriate drug therapy and a preventative exercise program.
Watch The Video for The Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases
What is EMG?
EMG, electromyography, is a special method used to diagnose nerve and muscle dysfunctions with a special device. The history of EMG test dates back to almost 100 years ago. In parallel with the developments in modern medicine, we have seen many new tests accumulated on the simple nerve and muscle measurements for the last 20-30 years. With the advancements of automatic devices, we are now able to run assays very quickly.
How To Perform EMG
EMG is composed of two main evaluations. Nerve conduction studies and needle EMG. These also include various tests. The physician performing EMG determines the tests. Needle EMG is not performed for every patient. Nerve conduction study is conducted with electrical impulses of short and low voltage. It basically covers all the procedures to measure electric conduction rate of the nerves. This way, the physician can test the function of motor and sensory nerves. For needle EMG, a needle electrode inserted directly into a muscle evaluates the muscle fibers and provides information on both the muscle and the relevant nerves.
How To Perform EMG ? Watch The Video
Who Can Perform EMG?
Only trained physiatrist or neurologists can perform EMG. EMG device can allow for many tests. Thus, in order to perform the majority of these tests a specialist must be trained for at least 2-3 years after BA. In some hospitals, technicians perform some of the EMG tests. Since it is a very dynamic test, it is highly undesirable for a technician to perform EMG without the supervision of a specialist.
Who Orders EMG?
Physical therapists, neurologists and neurosurgeons usually order EMG. Although not so often, other specialsts may also order EMG test.
How Does EMG Help Diagnosis?
EMG can provide direct diagnosis in many nerve and muscle diseases. In some cases, it is used to support or validate the diagnosis.
For The Diagnosis of Which Diseases is EMG Ordered?
EMG is ordered to help in the diagnosis of lumar and cervical disc herniations, muscle diseases (myopathy, muscular dystrophy), nerve diseases, nerve compressions, injury to nerves, sciatic nerve injury, neuromuscular transmission disorders, spinal cord disorders, facial palsy and some other nerve paralysis, idiopathic muscle weakness, hand and foot numbing, polyneuropathy secondary to diabetes.
Disorders That Can Be Diagnosed with EMG
Polyneuropathy (polyneutritis, Gullian Barre and polyneuropathy)
Carpal tunnel syndrome (nerve compression at the wrist)
Ulnar tunnel syndrome (nerve compression at the elbow)
Nerve root copmression due to spinal and cervical disc herniation
Nerve compression (entrapment neuropathy)
Perinatal nerve injuries
Nerve injury, crush and avulsions
Nerve involvement due to diabetes (polyneuropathy)
Motor neuron diseases (anterior horn disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis)
Congenital and developmental muscle diseases (myopathy, muscular dystrophy)
Nerve compression at the neck (thoracic outlet syndrome)
Cerebrospinal disorders (Multiple sclerosis, etc.) (evoked potentials VEP, BAEP, SEP)
How Long Does It Take To Perform EMG?
EMG is a dynamic test. The physician may prolong the test and perform additional evaluations. Thus, it may take 5 minutes to 1 hour. Test for a simple nerve compression may be completed in 5-10 minutes while test for anterior horn disease may take up to 1 hour.
Is EMG a Painful Procedure?
It depends on the physician’s experience. In the hands of an experienced specialist EMG is a painless test, but an unexperienced doctor can make this test painful for the patient. Electric conduction study can be easily performed even on children. The needle EMG, although not required for every patient, is not a challenging procedure if conducted carefully.
For The Tests Performed in Our Clinic, Please See Below.
Motor Nerve Conduction Tests
It can be classified as a standard test for each EMG procedure which is performed with the measurement of motor nerve conduction volocity. It provides significant information on cases of especially nerve compressions and polyneuropathy.
Sensory nerve conduction tests
Similar to motor nerve conduction tests, it is a standard test for each EMG procedure which is performed with the measurement of sensory nerve conduction velocity. It provides significant information on cases of especially nerve compressions and polyneuropathy.
Needle EMG
A needle electrode inserted directly into a muscle records the electrical activity in that muscle. This way, we can gather direct information on the muscle diseases and the related nerves. It is not a standard test for EMG procedure.
Repetitive Nerve Stimulation
It is a test for the diseases that effect neuromuscular transmission, such as myasthenia gravis. It is performed by imposing repetitive nerve stimulation.
Single Fiber EMG
It is a very sophisticated test for the diseases that effect neuromuscular transmission, such as myasthenia gravis. The electric activity of a single muscle fiber is examined. It requires a high level of experience.
Evoked Potentials: SEP
A test that records electrical activity of the brain resulting from the stimulation of sensory nerves on the legs and arms via the electrodes placed on the head. This way, the test studies if there is any dysfunction in spinal cord and neural pathways.
Evoked Potentials: Watch the SEP Video
F-wave and H.Reflex
These are auxiliary tests recording potentials produced upon the stimulation of nerves in the spinal cord. These are especially preferred for polyneuropathy and root compressions due to disc herniations.
Blink Reflex
It is a test used for facial palsy. It provides information on the fascial nerves and the recovery potential of fascial palsy.
Paravertebral Needle EMG
The evaluation of the muscles peripheral to spinal cord. It provides information on spinal and cervical disc herniation.
Anal Sphincter EMG
It is a needle EMG method testing anal sphincter for patients with fecal incontinence.
RecoveriX
RecoveriX; Stroke Therapy Based on Brain-Computer Interface
Stroke has become an imminent health condition among the elderly population. The patient loses the ability to move one side of the body secondary to embolism or hemorrhage. The most destructive effects of stroke occur on the arms and hands. Most of the patients continue to suffer from functional deficiencies called sequel upon conservative therapies like physiotherapy and relatively novel therapies like robotic treatments. There have been advancements on the treatment of stroke patients and neuro-technological therapies have started to provide benefit recently.
Brain-Computer Interface; Therapy By Power of Thought
Stroke can impair the patient’s ability to move their hands or arms but it cannot stop them from thinking about it. Basically the brain activity resulting from the thought of moving a body part is identical to the brain activity resulting from actually performing the movement. Based on this fact, RecoveriX, a new neuro-technological device to improve hand movements of stroke patients.
Various therapy methods for stroke are simultaneously administered in this method. The thought of movement (stimulating the movement center of the brain), special functional electrical stimulation to introduce movement and mirror therapy conducted by monitoring virtual hand movements on the screen are concurrently administered. This method differs from the earlier therapies with the use of the patient’s brain activity as a key. Thus, the EEG waves of the patient is integrated into the system. The computer is activated by the patient’s thought of moving (BCI – Brain Computer Interface).
This EEG based therapy is composed of two stages. At the first stage, analysis step, special electrodes that can stimulate the patient’s functioning and non-functioning hand. The patient wears a special EEG head that records brain waves produced while executing the movement or attempting to do so. A special computer program analyses the brain waves read by this head. At the second stage, the treatment step, the paralyzed patient attempts to move their hand upon the command of the device. If the patient’s brain waves are consistent with the movement attempted, the relevant hand is electrically stimulated to complete the movement. During this stage, the patient can monitor the movement by the reflection of their hand (avatar) on the screen. Which provides a visual feedback to the patient. This contributes to reconfiguring the functions of the brain during recovery to enable new movements and to improve the movements patients can already execute. This therapy can be combined with another neurotechnological method, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS – external stimulation of the brain neurons).
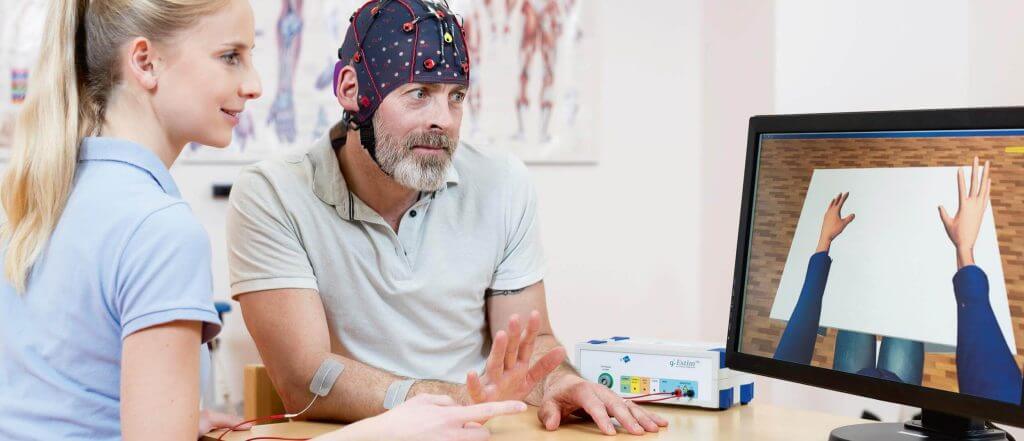
It is administered for 4 weeks on average. There are no side effects or contraindications of this therapy. This therapy can be administered in acute and chronic stroke cases and it can even provide positive outcomes for the patients that have been suffering for a long time.
You can see the video of RecoveriX Therapy below.
TMS – Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
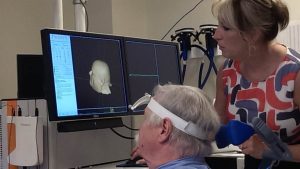
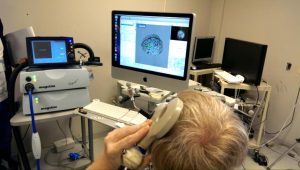
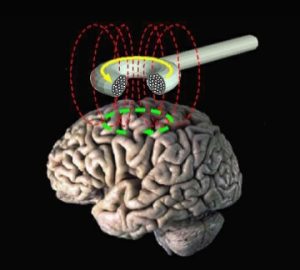 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation is a novel diagnostic and therapeutic method that is based on the principle of stimulating neurons through an external magnetic field. This method includes delivering magnetic current into specific parts of the brain. It is carried out with a special stimulation device and connected magnetic coils. It differs from the therapies directly inserted into the brain. Brain stimulation is externally performed without direct contact to the patient. Magnetic coil is approximated to the patient’s head. For magnetic brain stimulation, the magnetic current is delivered at a designated level of frequency.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation is a novel diagnostic and therapeutic method that is based on the principle of stimulating neurons through an external magnetic field. This method includes delivering magnetic current into specific parts of the brain. It is carried out with a special stimulation device and connected magnetic coils. It differs from the therapies directly inserted into the brain. Brain stimulation is externally performed without direct contact to the patient. Magnetic coil is approximated to the patient’s head. For magnetic brain stimulation, the magnetic current is delivered at a designated level of frequency.

How many sessions TMS can be administered?
TMS can be administered multiple times with at least 10 sessions depending on the disorder. Patient’s response to therapy is also important for determining the number of sessions. For some disorders, the therapy may even take months at certain intervals. The sessions usually take 20-30 minutes.
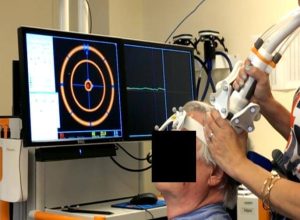
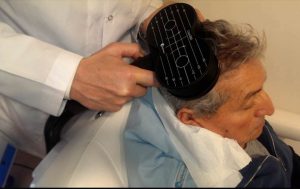
How Does The Patient Feel During TMS Therapy?
We must emphasize that TMS therapy is not a painful method. The patient will not feel any pain, but only hear a taping sound during the therapy. Thus, the patient is provided with an earplug during the therapy.
Are There Any Side Effects of TMS Therapy?
TMS therapy does not have any serious side effect. The most common side effects are headache and neck pain. Very rarely, epilepsy (epileptic seizure) cases have been reported. It is not a permanent damage for these cases. This side effect usually occurs in cases with very high frequencies for exploratory purposes and it does not occur in standard therapies performed within the safety guidlines.


Can TMS Therapy Be Used for Diagnostic Purposes?
TMS can provide beneficial information especially for diagnosis and follow-up of some brain and spinal cord diseases. It does provide valuable insight on how any lesion in spinal cord or brain affects neural functions, how these functions deteriorate or recover in time, indirectly. It is specifically very informative on disorders along with paralysis.
The Disorders for Which TMS Is Used
TMS Therapy is a novel therapy method. It is currently an FDA approved treatment choice for drug resistant depression covered by insurance agencies in USA. Furthermore, upon the outcomes of the studies conducted, it is now used in the treatment of neurological disorders. Its efficacy has been scientifically established for the treatment of some symptoms of hemiplegia (stroke, paralysis on one side of the body), Parkinson’s, tinnutus, speech disorders due to brain damage (aphasia), pain in spinal cord paralysis (paraplegia, spastic paraplegia). The efficacy on ataxia, chronic pain, fibromyalgia, and many other brain disorders affecting central nervous system (multiple sclerosis and degenerative brain disorders) is under research with mainly positive results. TMS therapy seems to become a standard therapy in the immediate future.
It has brought a whole new dimension to the treatment of disorders affecting central nervous system. To this day, the usual practice has been to administer medication and conventional rehabilitation methods for the treatment of brain disorders. In TMS therapy, directly neurons are stimulated. The studies conducted with recently advanced brain localization techniques (neuronavigation) and functional MRI suggest that TMS therapy will be most important treatment alternative for many incurable brain disorders in near future.
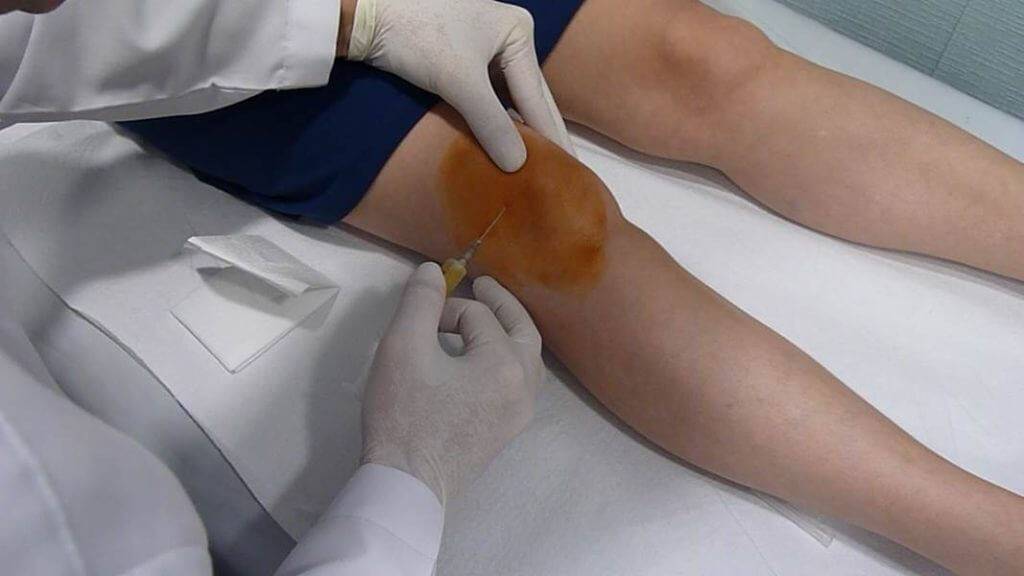
PRP
What is PRP Therapy?
PRP is a new natural therapy that has been increasingly used in various disorders especially for the last 5 years. Although it has originated as a cosmetic and anti-aging therapy, it is recently used in the treatment of musculoskeletal system disorders. PRP stands for “Platelet Rich Plasma”. The medication is prepared from the patient’s own blood.

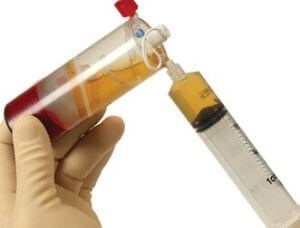
How to Obtain PRP
Approximately 10-20 cc of blood is drawn from the patient, based on the application. This blood is processed in specifically designed systems. The blood cells of the patient is centrifuged to achieve a platelet rich plasma fluid on the upper layer.
The Effect of PRP in The Body
Platelet is mainly the cell that provides coagulation and includes growth factor and some natural protectors. Platelet rich plasma operates as a natural medication. It speeds up the healing process of injured structures such as tendon, cartilage.
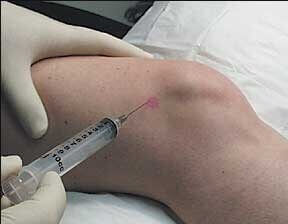
How Administered
It is injected into the treatment site 2-3 times usually with one month intervals with doses of 1-3 ml.
How to provide treatment for the patient with knee arthrosis Read more
PRP Application Areas
Knee osteoarthritis (Gonarthrosis): It is usually administered 3 times with monthly intervals.
Watch PRP Application
How to treat osteoarthritis of the hip joint? Read more
In the cases of osteoarthritis of the hip, shoulder and other joints: It is usually administered 3 times
Watch how to administer prp shoulder injection
Chronic tendinitis (tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow): It is usually administered 2 times.
Tendon injuries (Achilles tendinitis, adductor tendinitis, sports injuries): It is administered 1-3 times.
Rotator cuff tears: It is administered 1-2 times.
Are There Any Side Effects of PRP?
PRP method has no side effects. It may only cause temporary pain and swelling in the treatment site. This will go away in a couple of days and will not cause any permanent damage.
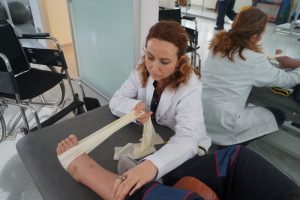
PRP Treatment in Ankle Cartilage Injury
Ankle sprain is one of the most common musculoskeletal system issues. This can occur both in athletes and ordinary people. One can experience ankle sprain both due to constraining in sports activities and also descending a ladder. Football matches are among the most common reasons for ankle cartilage problems in men. The fields with high friction is especially a great danger for under-exercised players. While walking on high heels is among the most common reasons for women.
Ankle is twisted inwards, in almost all cases, and this causes various levels of injuries on the lateral ligaments of the ankles. In mild injuries, the lateral ligaments are stretched. In severe injuries, these ligaments are torn. Patients may experience swelling and bruises on especially outer side of the ankle. The patient experiences pain when stepping on and has limited capacity of ankle movements. Usually putting ice on, resting, bandage and pain killers would provide sufficient efficacy in mild injuries. However, for severe injuries, the ankle may need to be stabilized with a brace or basic casts. Following the acute phase, physical therapy should be provided to accelerate recovery.
Patients with ankle sprains may experience a serious issue: A regional damage might occur on the articular cartilage of the ankle due to sprains, and this condition is called Osteochondritis. In “Talar Dome”, there is an articular cartilage injury and underlying bony involvement in the form of edema. In some cases, the injured part of the cartilage crumbles and bone is exposed in that area. Due to the deficiency of cartilage, corrosion starts in bones over the time and ankle arthritis, which is normally rare, occurs. This leads to permanent pain. In rare cases, a cartilage piece may fall into the joint spacing following ankle sprain. It requires arthroscopic removal procedure. If the patient experience permanent pain after the acute phase of ankle sprain, especially when stepping on and walking for an extended period of time, Osteochondritis should be taken into consideration. Osteochondritis in the ankle can only be diagnosed with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI examination also shows the degree of the injury.
Physical therapy can contribute to recovery of Osteochondritis by reducing the intra articular edema. Na hyalurinate injections administered intra-articularly into the ankle joint, increase the viscosity of the joints and prevents a certain level of damage to the joint.
Recently PRP therapy, prepared from the patient’s blood, is administered in cases of Osteochondritis. PRP stands for platelet rich plasma. PRP , concentration of platelets that are extracted from autologous blood, supports the injured cartilage to prevent crumbles in especially early phases of Osteochondritis, preventing ankle osteoarthritis in the long term. PRP is administered into the ankle joint at monthly intervals, 3 times in total, under USG. PRP may also be administered into the injured ligaments. PRP accelerates the recovery of the ligaments injured and strengthens the ligaments.
In all cases, special exercises for ankle should be done to support both PRP or other treatment methods. This can prevent a second ankle sprain, which is another great danger for these patients. If patient does not do preventive exercises, 30-70% of the cases the patient experiences a second ankle sprain. This may get so frequent to be defined as “chronic ankle sprain”. In this condition, the ankle loses its stability. In late phases, it may require surgical intervention.
Everyone may have an ankle sprain. The important thing is to take preventative cautions to avoid relapse. Osteochondritis should be taken into consideration in case of long term pain following the ankle sprain. Early diagnosis and the right treatment method can minimize the harm of Osteochondritis.
Plantar fasciitis, meniscal tear, osteochondritis, chronic bursts, ankle strain are among other areas of usage.
Neurological Rehabilitation
 Neurological disorders represent the widest area in rehabilitation medicine. Due to the lack of an effective medicinal treatment for the majority of the neurological disorders,
Neurological disorders represent the widest area in rehabilitation medicine. Due to the lack of an effective medicinal treatment for the majority of the neurological disorders,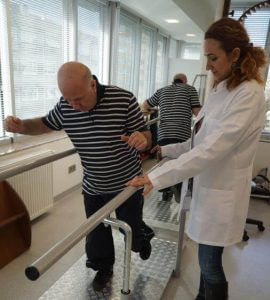 it is only possible through rehabilitation to maximize the patient’s functional capacity and to teach the patient how to leverage that capacity.
it is only possible through rehabilitation to maximize the patient’s functional capacity and to teach the patient how to leverage that capacity.
Neurological rehabilitation can be utilized in a number of primary disorders. Neurological rehabilitation is effective in patients suffering from stroke due to occlusion of an artery or bleeding into brain tissue (hemiplegia, stroke); traumatic brain injury; cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis; parkinson’s disease; spinal injuries (paraplegia; paraparesis); hereditary neurological disorders (polyneuropathy; degenerative brain disorders, ataxia); genetic or inherited muscle disorders (myopathies, muscular dystrophy); paralysis secondary to brain tumors and surgeries; Guillian-Barre syndrome; motor neuron disorders; patients who have fallen due to muscle weakness, imbalance and dizziness in old age.
Especially the conditions developed upon occlusion of an artery in brain, bleeding into brain or direct brain damage usually lead to paralysis on one side of the body. In these cases, the size of the area affected is the main factor for the recovery potential but rehabilitation also has a significant effect on the level of function for the future. Although medicinal therapy is essential for multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s diseases, which also have a high prevelance rate, there is a limit on the benefits of medicinal therapy. Medicinal therapy is not effective on spinal cord disorders, injuries and myopathies.
Patients are treated with neurological rehabilitation for falling due to muscle weakness, imbalance and dizziness in old age and exercise provides significant benefits for these types of patients. Essentially patients experience various changes due to low or no mobility in all neurological disorders that affect brain, spinal cord, nerves and muscles. Muscle weakness stands out among these disorders. Patient may also experience additional manifestations such as severe muscle spasticity, sensory loss, imbalance, involuntary movements. Medicinal therapies show little or no efficacy in such conditions. Medicines cannot strengthen the muscles for these patients. The patients mainly benefit from rehabilitation programs. These include various methods of therapy. Some of the methods used commonly for these patients can be listed as standard exercise methods (stretching, strengthening and balance exercises), special neurophysiological exercises, computer assisted rehabilitation therapies, and robotic rehabilitation. For patients with severe muscle spasticity, muscle relaxant botox injections are administered when necessary. Adjuvant equipments (orthesis) that streamlines walking may also be prescribed for eligible patients. These methods among many of the therapy options can maximize the patient’s level of function.
 The rehabilitation process should be initiated from day one. The important thing is to initiate the treatment process as soon as possible. After discharging from the hospital, the patient should continue treatment at home and start visits to physiotherapy centers when he/she is able to do so. If the patient is not able to visit the physiotherapy center, the physiotherapists should maintain the therapy process by visiting the patient at home and training the relatives about the process. It is extremely important for the family to involve in the treatment process in the cases of patients with cerebral palsy and patients that are not able to visit the physiotherapy center. It is really sad to encounter many patients who are confined to bed and their relatives simply because they are not provided with rehabilitation therapies in our country. The patients with neurological disorders, even when they are really old, should not be left to their fate. This would cause significant consequences for the patients and also their relatives.
The rehabilitation process should be initiated from day one. The important thing is to initiate the treatment process as soon as possible. After discharging from the hospital, the patient should continue treatment at home and start visits to physiotherapy centers when he/she is able to do so. If the patient is not able to visit the physiotherapy center, the physiotherapists should maintain the therapy process by visiting the patient at home and training the relatives about the process. It is extremely important for the family to involve in the treatment process in the cases of patients with cerebral palsy and patients that are not able to visit the physiotherapy center. It is really sad to encounter many patients who are confined to bed and their relatives simply because they are not provided with rehabilitation therapies in our country. The patients with neurological disorders, even when they are really old, should not be left to their fate. This would cause significant consequences for the patients and also their relatives.
Orthopedic rehabilitation
 Orthopedic rehabilitation covers all rehabilitation efforts performed following any type of orthopedic intervention (cast, surgical operation etc.) for the treatment of medical conditions due to a musculoskeletal disorder or trauma.
Orthopedic rehabilitation covers all rehabilitation efforts performed following any type of orthopedic intervention (cast, surgical operation etc.) for the treatment of medical conditions due to a musculoskeletal disorder or trauma.
Thus, orthopedic rehabilitation includes a wide scope. All cases of fracture; dislocation; joint stiffness and deformities due to cast and immobility; anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction; knee, hip and knee replacement; knee and hip arthroscopy; sports injuries; amputations (upper or lower extremity); Achilles tendon repair surgery; tendon and nerve repair surgeries in hands and feet; deformity correction surgery (hip dislocation, toe deformities etc) are among the common conditions that require orthopedic rehabilitation. Orthopedic rehabilitation is as important as the orthopedic surgery itself and has a direct impact on the success of the surgery. The common thread to all orthopedic interventions (cast, surgery, slings etc.) is the limitation on the mobility of the operation site. Human body is designed for continues mobility and severely harmed in cases of immobility. Soft tissue shortening and stiffness occurs on the restricted body parts. The level of the stiffness is directly proportional to the duration of immobility. Shortening and stiffness of the soft tissues result in joint stiffness and joint contractures.

This condition, “contracture”, is one of the main factors to define the success of the orthopedic intervention. Another significant issue we encounter upon orthopedic surgeries and the subsequent immobility is muscle weakness (atrophy). When muscles are not used for a month, approximately 30% is wasted on the muscular volume and strength. Thus, orthopedic rehabilitation targets these two main conditions, joint stiffness and atrophy, occurring on the joints and peripheral body parts due to long term inactivity. Currently, the subsequent inactivity period is one of the main elements for the choice of bone & joint surgeries and also tendon surgeries. For example, in the case of a femoral fractures, intraosseous nailing is preferred over plaster casts. For plaster cast, the treatment period (bone union) extends to 2-3 months and upon the removal of the cast, the patient may be left with incurable joint stiffness, especially on the knees. Fır intraosseous nailing, the patient can resume their daily activities after a short period of time and bone union is achieved much faster. Since this method allows a limited level of activity, the patient does not suffer from joint stiffness.

Unfortunately, there are quite many orthopedists in our country who still has not fully comprehended the significance of orthopedic rehabilitation. They do not recommend rehabilitation after the removal of plaster casts and surgeries to the patients and in some cases they just suggest home exercises. Nevertheless, it is not possible for the patients to recover the damage with just home exercises. In the cases of some special surgeries, such as tendon surgeries, physical therapy is indispensable. The longer it takes to initiate the rehabilitation program after any orthopedic intervention, the harder it gets to recover from the joint stiffness occurred due to inactivity. Please note that all orthopedic interventions require rehabilitation and rehabilitation is a significant factor for the outcome of the therapy.
What is Physical Therapy?
Physical therapy means the application of physical agents such as heat, light, electric, ultrasound, laser, electromagnetic field, pressure for musculoskeletal nervous system disorders. The number of physical therapy applications arise in line with the advancements in modern medicine.It is of the physician’s choice to use physical therapy agents as monotherapy or in preparation phase for exercise or rehabilitation.
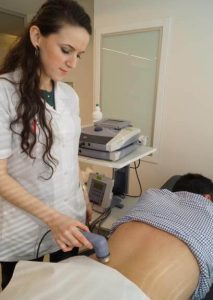
Short Wave Diathermy
A treatment method where high frequency Electromagnetic waves are used to generate deep heat on body tissues. It is primarily used in treatments regarding joints.
Infrared Therapy
A treatment method where infrared waves are used to generate heat on superficial tissues. Provides a warm relaxing effect.
Paraffin Treatment
Paraffin treatment is a special heat treatment where the patient soaks their hands in paraffin liquefied with a special device. It is especially preferred in conditions such as osteoarthritis, trigger finger, nerve compression of hand.
Electrotherapies
A treatment method where various frequencies of electric current submitted to the patient. These are TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) therapies and interference current are mostly used. These therapies are preferred in almost all painful musculoskeletal conditions. Provides pain relief and analgesic effects.
Vacuum Treatment
Negative pressure therapy via special devices that provides a vacuum effect on the skin. Most of the devices apply low-frequency current to application site concomitantly with the vacuum. Blood accumulates on the specified site, utilizing the curative effect of the blood and the analgesic effect of the current. It can be applied in almost all painful conditions.
Traction (Decompression Therapy)
Traction, i.e. decompression therapy, is based on the principle of applying bilateral traction on the spinal cord with the help of an electromechanical system for the treatment of lumbar and cervical disc herniation, spondylosis. This provides spacing between the vertebral bodies and retract herniation and relief of the compressed the nerves.
Electrical Muscle Stimulation
It is based on the principle of recruiting weak muscles via electric impulses. It is a highly efficient treatment agent for the cases of muscle weakness due to nerve damage or non-use. It is frequently preferred for the rehabilitation of patients with paralysis and also injured athletes.
Laser Treatment
Laser beams are used in superficial musculoskeletal and tendon conditions. Laser treatment is mostly preferred for nerve compression, tendinitis and bursitis. Provides relief and analgesic effects.
Pneumatic Compression Therapy (Vazotrain-Pneumatic Jabs)
This method is preferred for leg swelling due to lympoedema and venous stasis. A special boot is used to apply intermittent pressure to patient’s legs for reducing swelling.
EMG Biofeedback
It is based on the principle of transmitting the signals from the muscles into a monitor during exercise and making the patient to view those signals. This way, the patient can observe how efficient they can use their muscles and get further encouraged.
Iontophoresis
It is used to treat excessive sweating on the hands and feet by means of galvanic current to water in cannisters. This is a highly efficient treatment for excessive sweating on the hands and feet, with applications at certain intervals.
CPM (Continuous Passive Motion) Device
A method used for reducing the level of joint stiffness especially after orthopedic surgeries. The device, upon angle and speed adjustments, provides continuous motion of the targeted joint. Thus, accelerates rehabilitation process and eliminates joint stiffness.

